Tetsuro Aita, Postdoctoral fellow

Associate professor, Department of General Internal Medicine and Family Medicine / Center for General Internal Medicine and Family Medicine
Tetsuro Aita
Tetsuro Aita, MD, PhD, FACP
Dr. Tetsuro Aita joined the Department of Clinical Epidemiology as a graduate student in April 2021. He was born in Yamagata Prefecture in 1987 and graduated from Fukushima Medical University with an MD degree in 2012. He completed a doctoral course and earned a PhD degree in March 2024. He also enrolled in the Master of Epidemiology program at the London School of Hygiene and Tropical Medicine in October 2023. Currently, Dr. Aita works as an associate professor in the Department of General Internal Medicine and Family Medicine / Center for General Internal Medicine and Family Medicine at Fukushima Medical University.
“I have trained as a general internal medicine physician in diverse medical settings, including remote areas, isolated islands, community hospitals, and a university hospital. My experiences working closely with patients in these varied environments deepened my commitment to advancing patient care and solving practical challenges in clinical medicine. This commitment led me to join the Department of Clinical Epidemiology to focus on my studies. During my time as a graduate student, I successfully published relevant clinical research addressing questions from the clinical field to a global audience, including publications in Emerging Infectious Diseases (2023) and International Journal of Infectious Diseases (2023). Moving forward, I aim to continue disseminating impactful research that bridges clinical practice and evidence-based solutions. Additionally, I aspire to mentor the next generation of clinical researchers by teaching and fostering skills in clinical epidemiology, contributing to a culture of inquiry and evidence-driven medicine.”
[Academic affiliations and certifications]
- The Japanese Society of Internal Medicine (Fellow)
- Fellow of the American College of Physicians
- Japan Primary Care Association
- Japanese Society of Hospital General Medicine (Board Member)
- The Japanese Association for Infectious Diseases
- Society for Clinical Epidemiology
[Residency and clinical experience]
- 2012: Junior Resident, Okinawa Chubu Hospital
- 2014: Department of General Internal Medicine, Okinawa Chubu Hospital
- 2016: Department of General Internal Medicine, Okinawa Hokubu Hospital
- 2017: Department of General Internal Medicine, Fukushima Medical University Hospital
- 2024: Department of General Internal Medicine and Family Medicine
- 2024: Center for General Internal Medicine and Family Medicine
[Selected Clinical Research]
-
-
-
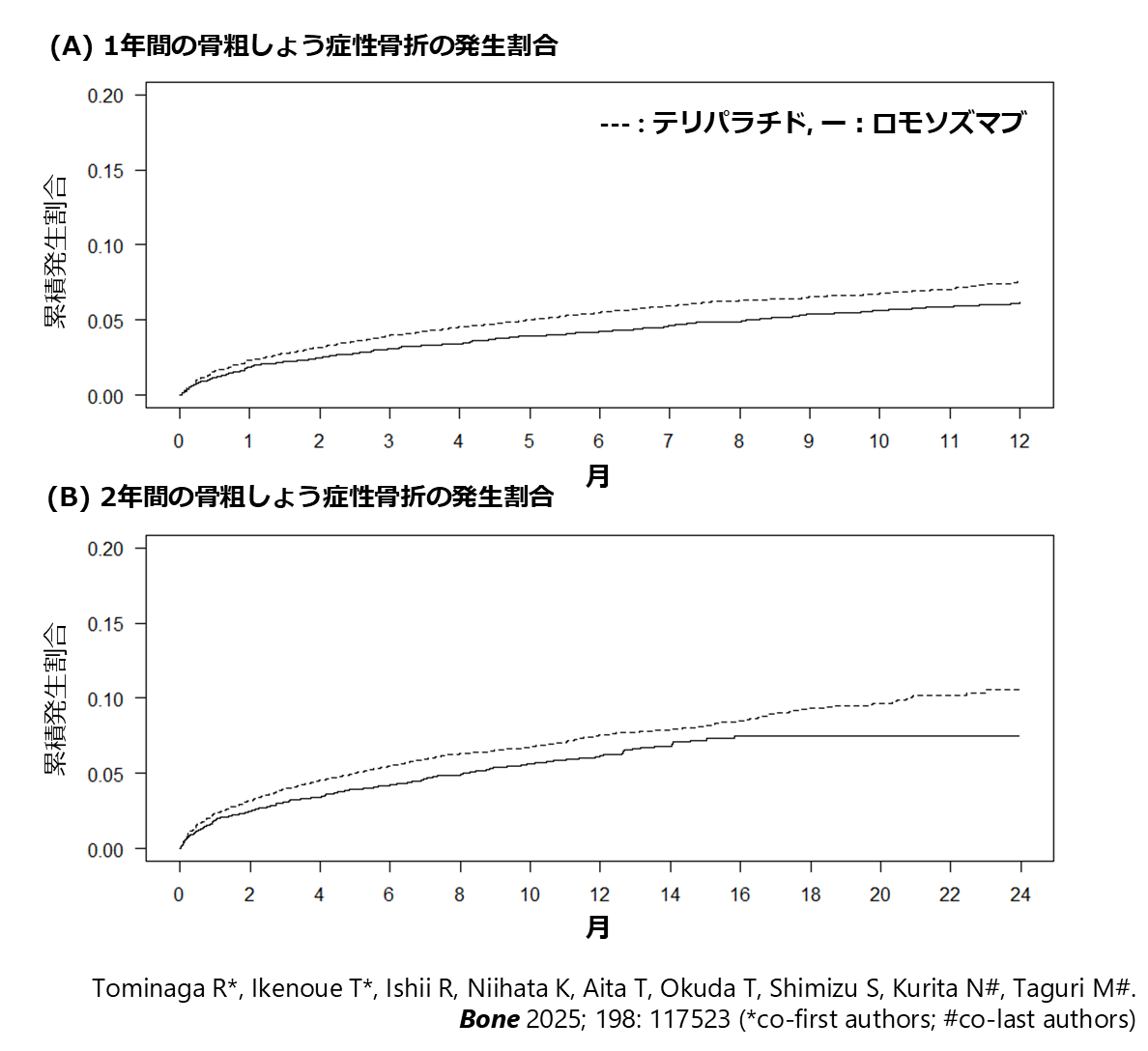
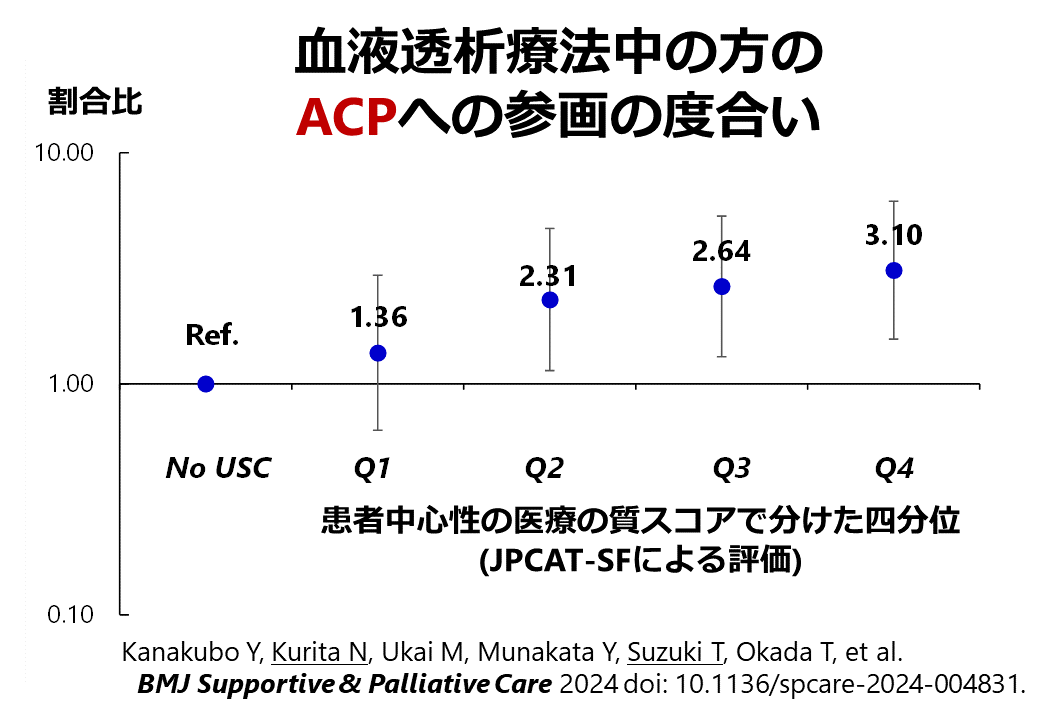
Kanakubo Y, Kurita N#, Ukai M, Aita T, Inanaga R, Kawaji A, Toishi T, Matsunami M, Munakata Y, Suzuki T, Okada T. (#corresponding author)血液透析における人を中心に据えた医療の質とアドバンスケアプランニングへの参加との関連性BMJ Supportive & Palliative Care 2024; 14: e2872-e2879. doi:10.1136/spcare-2024-004831
-
Inanaga R, Toida T, Aita T, Kanakubo Y, Ukai M, Toishi T, Kawaji A, Matsunami M, Okada T, Munakata Y, Suzuki T, Kurita N#. (#corresponding author)血液透析患者における医師への信頼、多次元ヘルスリテラシー、服薬アドヒアランスの関係性Clinical Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 2024; 19: 463-471. doi:10.2215/CJN.0000000000000392
日本の血液透析患者を対象に質問紙調査を行い、健康に関する情報を入手して適切に活用する力(ヘルスリテラシー)が服薬を指示通りに続ける程度(服薬の遵守度)にどのように影響するか、またこの影響が医師への信頼度によってどのように中継されるかを調査しました。
その結果、機能的なヘルスリテラシーと伝達的なヘルスリテラシーは、服薬の遵守度と良い関係があることが分かりましたが、批判的なヘルスリテラシーが高いと服薬の遵守度が低下する傾向がありました。さらに、これらのヘルスリテラシーと服薬の遵守度の関係は、医師への信頼によって中継される可能性が示されました。言いかえると、健康情報を理解する力が高いほど、服薬の遵守度が高くなりますが、これは医師の治療の説明などに対する信頼が役割を果たしており、信頼するほど医師の指示通りに服薬を続けられる傾向があるという考えを、研究が支持しました。
この結果から、血液透析患者の服薬の遵守度を向上させるためには、適切なヘルスリテラシーに対応したアプローチだけでなく、医師との信頼関係の構築も重要であることが確認できました。[※研究成果が、福島民報 日刊に掲載されました。福島医大 人工透析患者の服薬行動調査 効用に懐疑で中断の傾向 稲永医師、栗田特任教授のチーム. 福島民報. 2024年1月31日 日刊21ページ. また、研究成果が、福島民友 日刊に掲載されました。医療情報 積極収集する患者 服薬順守度高く 福島医大の稲永医師ら調査. 福島民友. 2024年1月31日 日刊19ページ.]
-
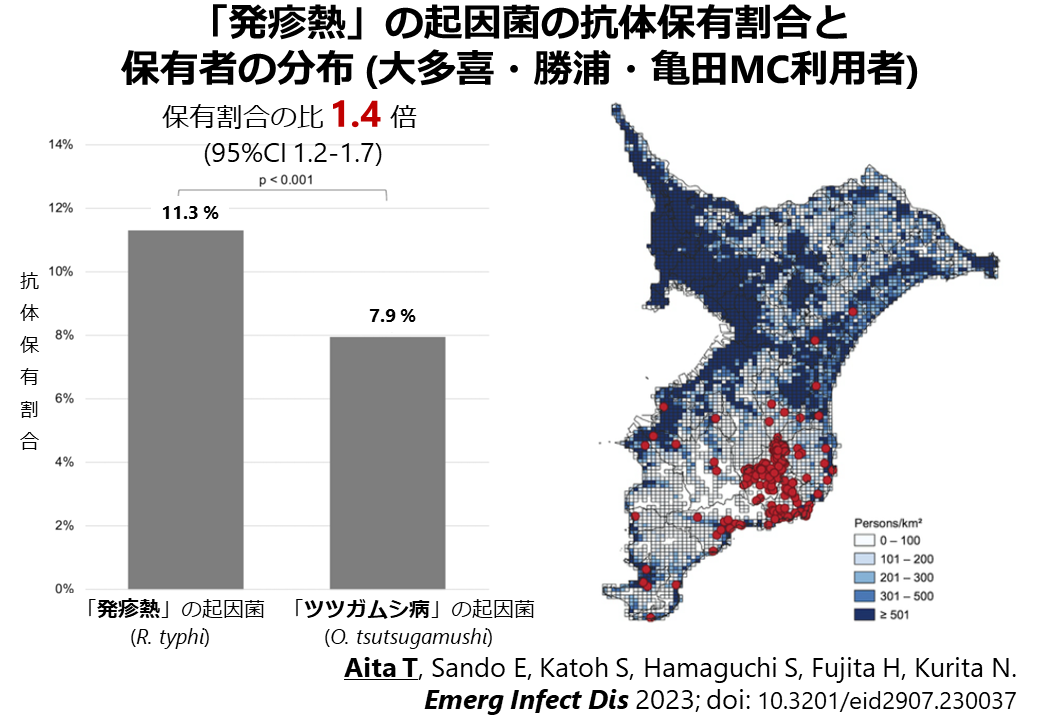
Aita T, Sando E, Katoh S, Hamaguchi S, Fujita H, Kurita N日本における発疹熱(murine typhus)の血清有病率とその予測因子:大規模な血清疫学研究Emerging Infectious Diseases 2023; 29: 1438-1442. doi:10.3201/eid2907.230037
「発疹熱」の日本での報告は稀ですが、2020年8月から11月にかけて、房総半島南部の2,382人の住民を対象に、この疾患の疫学を明らかにするための調査を行いました。原因菌であるRickettsia typhiの血清有病率と、同時に「ツツガムシ病」として知られる病気の病原菌であるOrientia tsutsugamushiの血清有病率も調査しました。驚くべきことに、Rickettsia typhiの血清有病率はOrientia tsutsugamushiの1.4倍も高いことがわかりました。これにより、「発疹熱」が現代において、発生はしていても注目されていない病気であることが示唆されました。この研究は、総合内科・臨床感染症学講座の山藤教授がリードしたプロジェクトで、大学院生の會田先生が筆頭著者として参画しました。主指導教員は、主要評価項目の解析やリスク因子の解析と結果の見せ方、論文の書き方で力を注ぎました。[※本研究の成果が、福島民報 日刊に掲載されました。「発疹熱」見逃されている恐れ 福医大研究チーム発表 適正診断へ実態解明急ぐ. 福島民報. 2023年8月5日 日刊27ページ. 福島民友 日刊に掲載されました。発疹熱見逃しか 高い抗体保有率 積極的な検査を 福島医大研究成果. 福島民友. 2023年8月4日 日刊23ページ.]
-
Aita T, Sando E, Katoh S, Hamaguchi S, Fujita H, Kurita N日本におけるリケッチア感染症の紅斑熱グループと発疹熱グループの血清学的交差反応性International Journal of Infectious Diseases 2023; 130: 178-181. doi:10.1016/j.ijid.2023.03.012
この研究は、日本紅斑熱(感染症法で四類感染症に指定されています。原因菌はRickettsia japonicaです。)という病気を確定診断された人々の血清が、発疹熱という別の病気の原因菌であるRickettsia typhiの抗体検査に対して交差反応をする頻度を調べたものです。その結果、約20%の症例で交差反応が確認されました。しかし、ペア血清中の両方のIgM/IgG力価を比較することで正確に診断できる症例があり、鑑別困難な症例は全体の5.6%にとどまりました。この研究は、総合内科・臨床感染症学講座の山藤教授がリードしたプロジェクトで、大学院生の會田先生が筆頭著者として参画しました。主指導教員は、主要評価項目の解析や結果の見せ方、論文の書き方で力を注ぎました。[※本研究の成果が、福島民報 日刊に掲載されました。福医大の研究チーム 「日本紅斑熱」患者の抗体の2割 「発疹熱」の抗体と誤認される可能性. 福島民報. 2023年5月17日 日刊3ページ.また、福島民友 日刊に掲載されました。感染症の抗体 誤認恐れ 福島医大発表 日本紅斑熱と発疹熱. 福島民友. 2023年5月18日 日刊19ページ.]

[Selected Conference Presentation]
Aita T, Kurita N, Katoh S, Hamaguchi S, Sando E.
Non-negligible seroprevalence of murine typhus and its predictors in Japan: a large-scale seroepidemiological study
ACP Internal Medicine Meeting 2022, Apr 28, 2022; Web/Chicago