Ryohei Inanaga, Graduate student

Graduate student
Ryohei Inanaga
Ryohei Inanaga, MD
Dr. Ryohei Inanaga joined Department of Clinical Epidemiology as a graduate student in October 2022. Dr. Inanaga was born in Kanagawa Prefecture in 1987. Dr. Inanaga graduated from Kyorin University and earned a MD degree in 2013. He is currently working at Department of Nephrology, Shin-yurigaoka General Hospital.
“For the past 10 years, I was engaged in medical care as a nephrologist both at a university hospital and community hospitals. In recent renal failure care, patients are aging and their pathological conditions and social backgrounds are becoming more complicated. Therefore, in order to clarify the nature of renal failure, and to conduct research that can serve as a bridge between patients and medical professionals, I have decided to enter the Department of Clinical Epidemiology. I will continue to work hard so that I can publish valuable clinical research.”
[Academic affiliations and certifications]
The Japanese Society of Internal Medicine(Fellow and Board Certificated member)
Japanese Society of Nephrology(Board Certified Nephrologist)
Member of Japanese Society for Dialysis Therapy
Member of Japanese Society for Peritoneal Dialysis
Member of Japan College of Rheumatology
Infection Control Doctor
[Residency and clinical experience]
2013- Junior resident, Kyorin University Hospital
2015- Department of Nephrology and Rheumatology, Kyorin University School of Medicine
2017- Nephrology Center, Toranomon Hospital Kajigaya
Department of Internal Medicine, Shirakawa Hospital
2018- Department of Nephrology, Shin-yurigaoka General Hospital
[Clinical research]
-
Niihata K*, Kurita N*#, Inanaga R, Toida T, Abe M, Masaki T, Yamamoto S. (*co-first authors; #corresponding author)Long-Term Frailty Progression and Mortality in Hemodialysis: Impact of Dialysis Duration and Baseline Frailty in a Nationwide Japanese CohortClinical and Experimental Nephrology 2026; (in press)
-
Inanaga R, Toida T, Aita T, Kanakubo Y, Ukai M, Toishi T, Kawaji A, Matsunami M, Okada T, Munakata Y, Suzuki T, Kurita N.Journal of Nephrology 2026; doi:10.1093/joneph/aajag041 (in press)
-
Yamaguchi T, Takahashi N, Inanaga R, So R, Kikuchi H, Noma H, Sasai H, Kamada K, Sugimoto T, Tsushima H, Ichikawa T, Miyake H, Fujita S, Ono K, Miwa Y, Hasegawa A, Suzuki N, Onishi A, Matsui T, Watanabe R, Hasegawa Y, Ono R, Isozaki T, Ishikawa Y, Yajima N, Kurita N.JMIR Research Protocols 2025; 14: e78612. doi:10.2196/78612
-
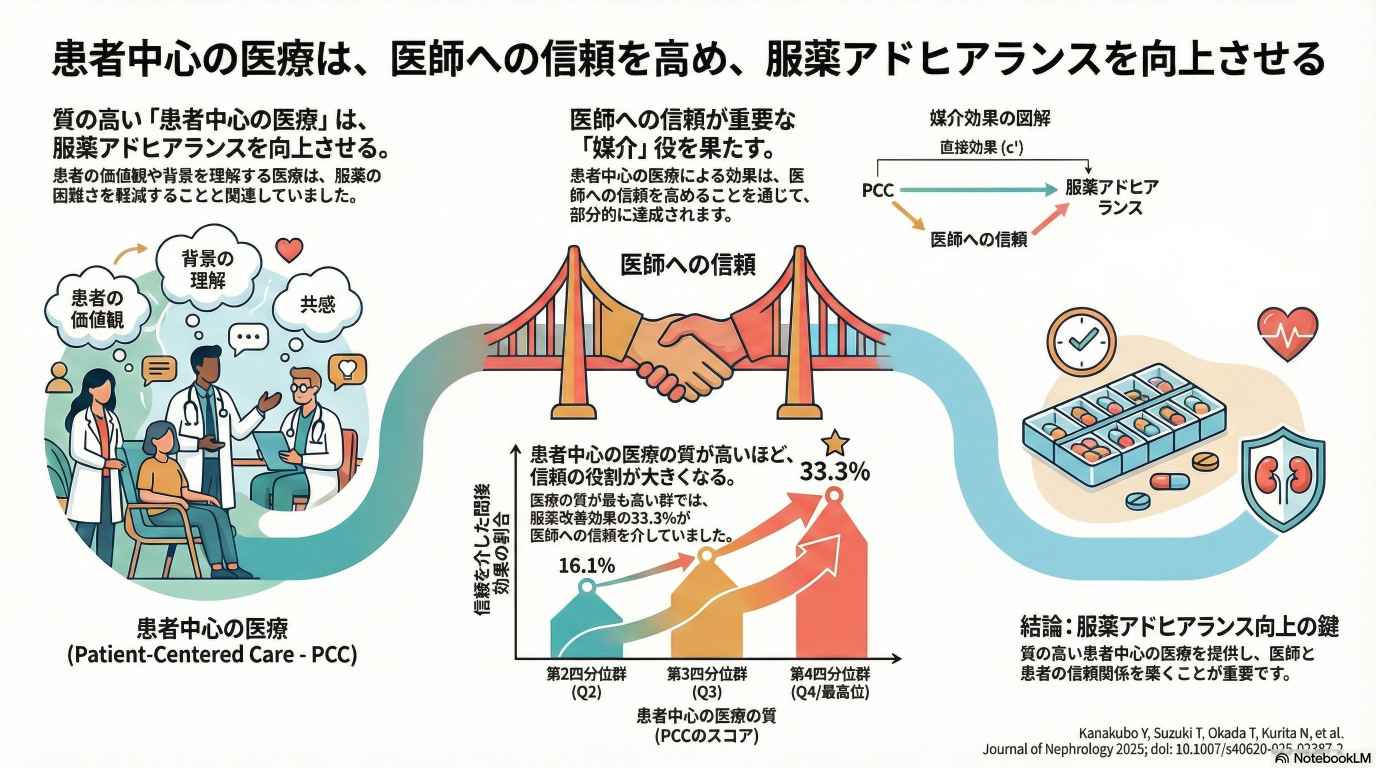
Kanakubo Y, Inanaga R, Toida T, Aita T, Ukai M, Kawaji A, Toishi T, Matsunami M, Munakata Y, Suzuki T, Okada T, Kurita N#. (#last author)Journal of Nephrology 2025; 38: 2273–2283. doi:10.1007/s40620-025-02387-2
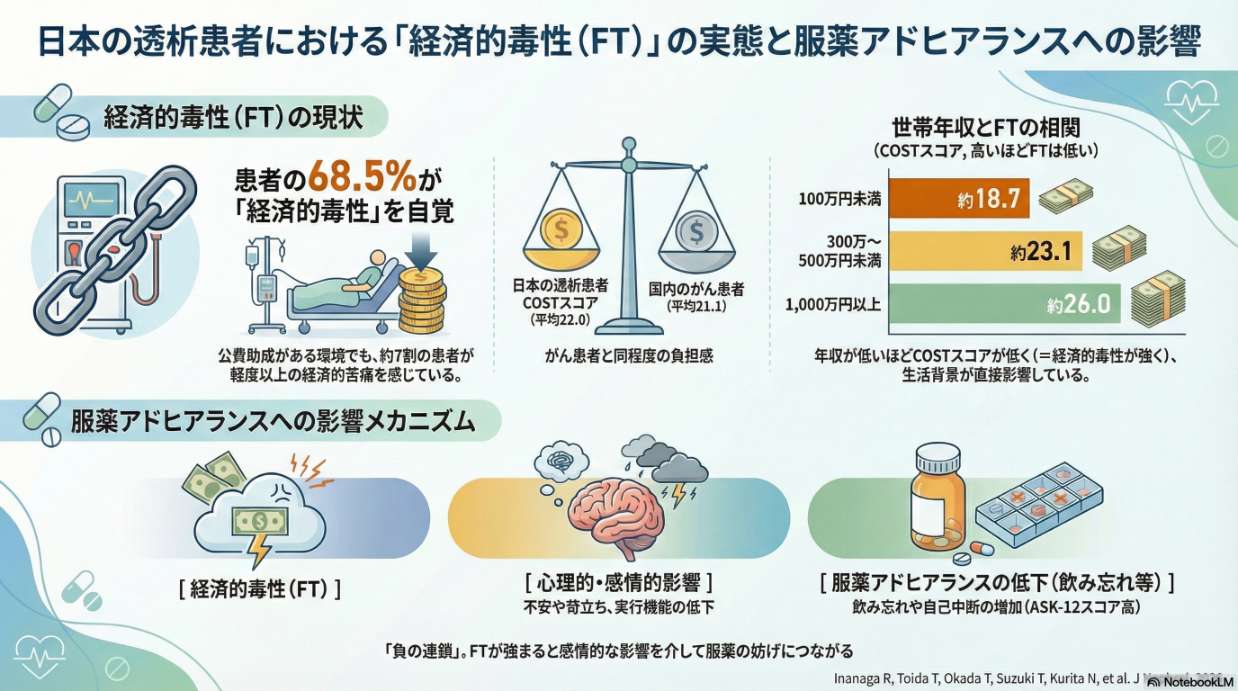
「人を中心に据えた医療」や「医師への信頼」が透析患者の服薬アドヒアランスに影響することが経験的に知られていますが、それらがどのように服薬アドヒアランスにつながるのかが明らかではありませんでした。日本の6施設に通院する血液透析患者を分析した結果、「人を中心に据えた医療の質」が高いほど服薬の困難度は少なく、その関連は「医師への信頼」の高さを通じて部分的に媒介されていました。特に質が最も高い群では、服薬アドヒアランスへの影響の約3分の1が「医師への信頼」を介したものでした。本研究は、透析患者の服薬アドヒアランス向上のためには、信頼関係の構築やケアの継続性・ケアの連携を含む多面的な「人を中心に据えた医療アプローチ」が重要であることを示しています。科学研究費補助金の助成(基盤研究(B) 課題番号JP19KT0021 および 挑戦的研究(萌芽) 課題番号JP22K19690; 研究代表者:栗田; 基盤研究(C) 課題番号23K16271; 研究代表者:戸井田)を受けた研究の成果(チームプロダクト)です。[※論文はこちらよりご覧頂けます。]
-
Joki N, Toida T, Niihata K, Inanaga R, Nakata K, Abe M, Hanafusa N, Kurita N#. (#last author)Hypertension Research 2025; 48: 2045–2057. doi:10.1038/s41440-025-02231-x
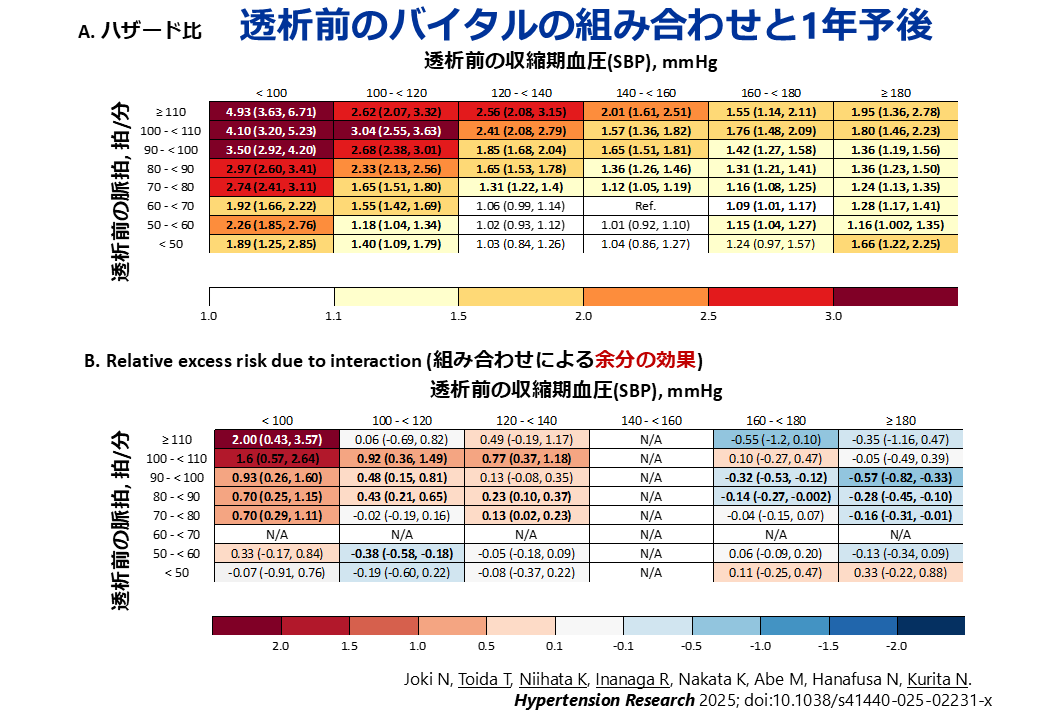
透析患者における予後評価の指標として、透析前の収縮期血圧(SBP)や脈拍数は広く用いられていますが、それぞれを個別に評価するだけでなく、両者を組み合わせて評価することが予後にどのような影響を与えるかは、これまで十分に検討されていませんでした。本研究では、日本透析医学会が実施する全国透析データベース(Japanese Renal Data Registry)を用いて、維持血液透析を受けている275,215名の患者を対象に、透析前のSBPと脈拍数の組み合わせが1年以内の死亡リスク、心疾患による死亡リスクの予測において、どの程度有用であるかを検討しました。
その結果、SBPが低い場合には、脈拍数に関係なく全死亡リスクが高まる傾向が認められました。また、SBPと脈拍数を組み合わせて評価するモデルは、それぞれを単独で評価するモデルよりも、全死亡および心血管死の予測において統計学的に優れていることが明らかになりました。特に、低いSBPまたは高い脈拍数の組み合わせにおいて、相加的・相乗的なリスクの増加が観察されました。
これらの結果は、透析前に日常的に測定される血圧と脈拍というシンプルな指標を組み合わせて評価することで、単独評価では見逃される可能性のある高リスク患者の層別化が可能になることを示唆しています。臨床現場における予後予測や治療方針の決定において、より精緻なリスク評価ツールとして活用するためのさらなる研究が求められます。
東邦大学の常喜教授と共に研究課題を発案し、博士研究員の戸井田先生・新畑先生と主指導教員が解析論文化でコミットしました。[※論文はこちらよりご覧頂けます。]
-
Shibagaki Y, Sofue T, Kawarazaki H, Toida T, Suzuki T, Nishiwaki H, Asano K, Terawaki H, Ito T, Oka H, Nagai K, Murakami M, Nagai K, Komukai D, Adachi T, Furukata S, Tsutsui T, Fujisaki K, Sugitani S, Shimizu H, Nishino T, Asada H, Shimizu H, Tsukamoto T, Nakaya I, Yamada Y, Inanaga R, Yamada S, Nakanishi S, Maeda A, Yamamoto M, Hirashio S, Okamoto T, Nakamura T, Miyoshi K, Kado H, Toda S, Shibata S, Nishi K, Yamamoto M, Naganuma T, Zamami R, Furusho M, Miyasato H, Tamura Y, Raita Y, Fukuhara C, Uehara K, Inoue K, Taki Y, Nakano N, Kurita N#, and the PREPARES Study Group. (#last author)Kidney International Reports 2025; 10: 2778-2788. doi:10.1016/j.ekir.2025.05.011
腎代替療法の選択は、患者の生活に大きな影響を与える重要な場面であり、患者と医療者が協力して意思決定を行う「協働意思決定(Shared Decision-Making:SDM)」が推奨されています。しかし、日本におけるCKD(慢性腎臓病)患者のSDMに対する理解や実際の経験、そしてSDMが行われたという認識に影響を与える要因については、これまで十分に明らかにされていませんでした。
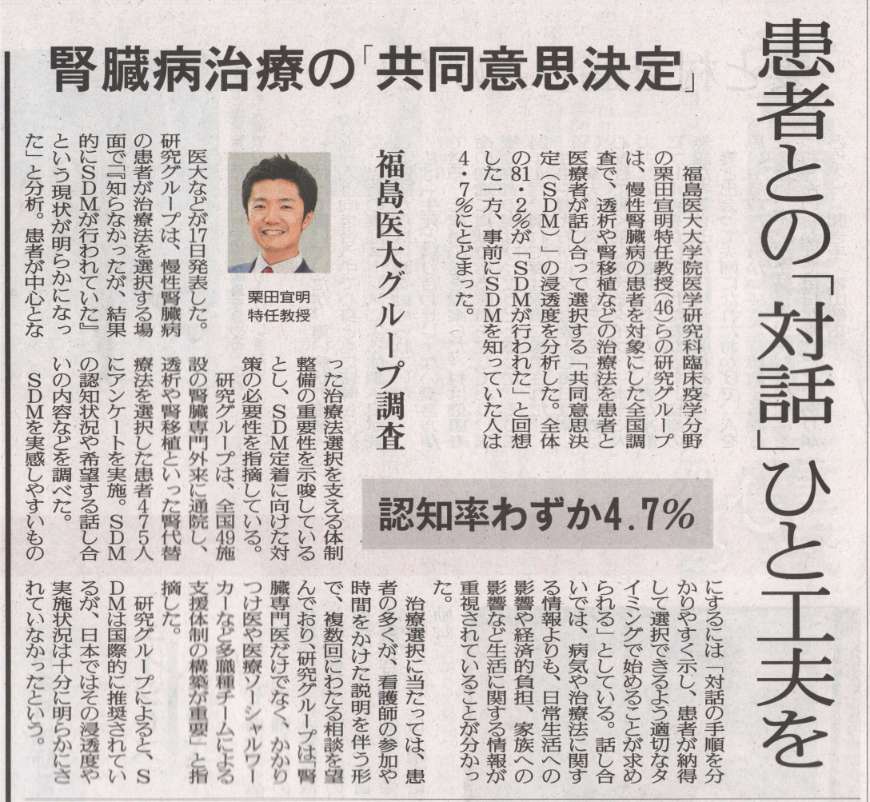
そこで本研究では、全国49施設の成人CKD患者475名を対象に、腎代替療法を選択した際のSDMに関する調査を行いました。その結果、全体の8割以上が腎代替療法選択時にSDMが行われたと感じていた一方で、調査前からSDMという概念をよく知っていた人はわずか4.7%でした。患者が特に重視したい話題は、「日常生活への影響」「経済的負担」「家族との関係」などで、多くの人が「腎代替療法が必要になる直前」に「複数回にわたる話し合い」の実施を望んでいました。また、腎臓専門医だけでなく、医療ソーシャルワーカーやかかりつけ医(非腎臓専門医)など、さまざまな医療職の関与も重視されていました。SDMの認識と有意に関連していたのは、腎代替療法選択のための外来(看護師の参加と十分な時間が確保された外来)への複数回の受診でした。本研究の結果より、日本の腎代替療法選択において患者は自身の生活に直結する情報を求めており、繰り返しSDMの機会を設ける体制の整備が、今後のCKD診療においてますます重要になると考えられます。
科学研究費補助金の助成(基盤研究(C) 課題番号JP21K10314; 研究代表者:柴垣; 基盤研究(B) 課題番号JP19KT0021 および 挑戦的研究(萌芽) 課題番号JP22K19690; 研究代表者:栗田)を受けたPREPARES研究(PREference for PAtient REnal replacement therapy and Sharing Study)の成果(チームプロダクト)です。主筆は、聖マリアンナ医科大学の柴垣教授が務められました。主指導教員は、ロジスティクスを含めた研究計画の立案・解析・論文化支援でフルコミットし、日本全国の50の施設でご活躍の腎・透析専門医の先生方とチームで推進しました。[※研究成果が、福島民友 日刊に掲載されました。患者との「対話」ひと工夫を 腎臓病治療の共同意思決定、福島医大グループ調査. 福島民友. 2025年6月18日 日刊3ページ.]
-
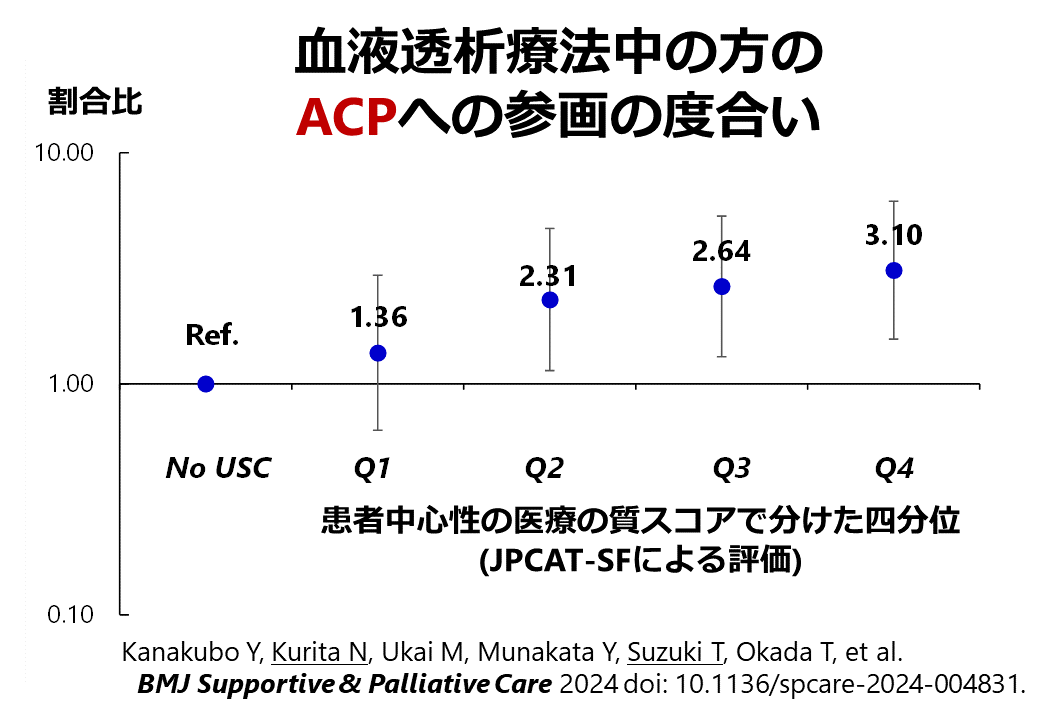
Kanakubo Y, Kurita N#, Ukai M, Aita T, Inanaga R, Kawaji A, Toishi T, Matsunami M, Munakata Y, Suzuki T, Okada T. (#corresponding author)血液透析における人を中心に据えた医療の質とアドバンスケアプランニングへの参加との関連性BMJ Supportive & Palliative Care 2024; 14: e2872-e2879. doi:10.1136/spcare-2024-004831
-
Inanaga R, Toida T, Aita T, Kanakubo Y, Ukai M, Toishi T, Kawaji A, Matsunami M, Okada T, Munakata Y, Suzuki T, Kurita N#. (#corresponding author)血液透析患者における医師への信頼、多次元ヘルスリテラシー、服薬アドヒアランスの関係性Clinical Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 2024; 19: 463-471. doi:10.2215/CJN.0000000000000392
日本の血液透析患者を対象に質問紙調査を行い、健康に関する情報を入手して適切に活用する力(ヘルスリテラシー)が服薬を指示通りに続ける程度(服薬の遵守度)にどのように影響するか、またこの影響が医師への信頼度によってどのように中継されるかを調査しました。
その結果、機能的なヘルスリテラシーと伝達的なヘルスリテラシーは、服薬の遵守度と良い関係があることが分かりましたが、批判的なヘルスリテラシーが高いと服薬の遵守度が低下する傾向がありました。さらに、これらのヘルスリテラシーと服薬の遵守度の関係は、医師への信頼によって中継される可能性が示されました。言いかえると、健康情報を理解する力が高いほど、服薬の遵守度が高くなりますが、これは医師の治療の説明などに対する信頼が役割を果たしており、信頼するほど医師の指示通りに服薬を続けられる傾向があるという考えを、研究が支持しました。
この結果から、血液透析患者の服薬の遵守度を向上させるためには、適切なヘルスリテラシーに対応したアプローチだけでなく、医師との信頼関係の構築も重要であることが確認できました。[※研究成果が、福島民報 日刊に掲載されました。福島医大 人工透析患者の服薬行動調査 効用に懐疑で中断の傾向 稲永医師、栗田特任教授のチーム. 福島民報. 2024年1月31日 日刊21ページ. また、研究成果が、福島民友 日刊に掲載されました。医療情報 積極収集する患者 服薬順守度高く 福島医大の稲永医師ら調査. 福島民友. 2024年1月31日 日刊19ページ.]